CNC Turning
CNC Turning
At PREPART CNC turning parts can be produced as little as 1-3 days!
We provide over 20 material options in stock including Plastic, Metal rods.
PREPART offers efficient CNC turning services with competitive price. You’ll get high-quality CNC turned parts with requirements you need.
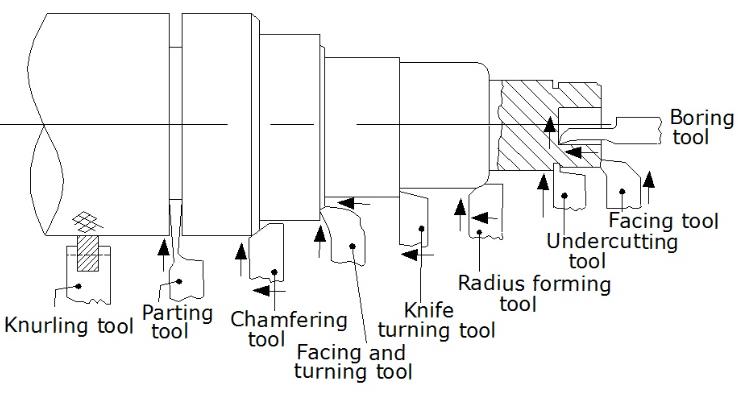
CNC/CNC Lathe Turning is a manufacturing process wherein metal round stock is held in a chuck on a spindle and rotated while a cutting tool is fed to the bar stock to remove material in order to create a desired shape, is an effective way to make cylindrical parts, as well as other shapes, including squares or hexagons.
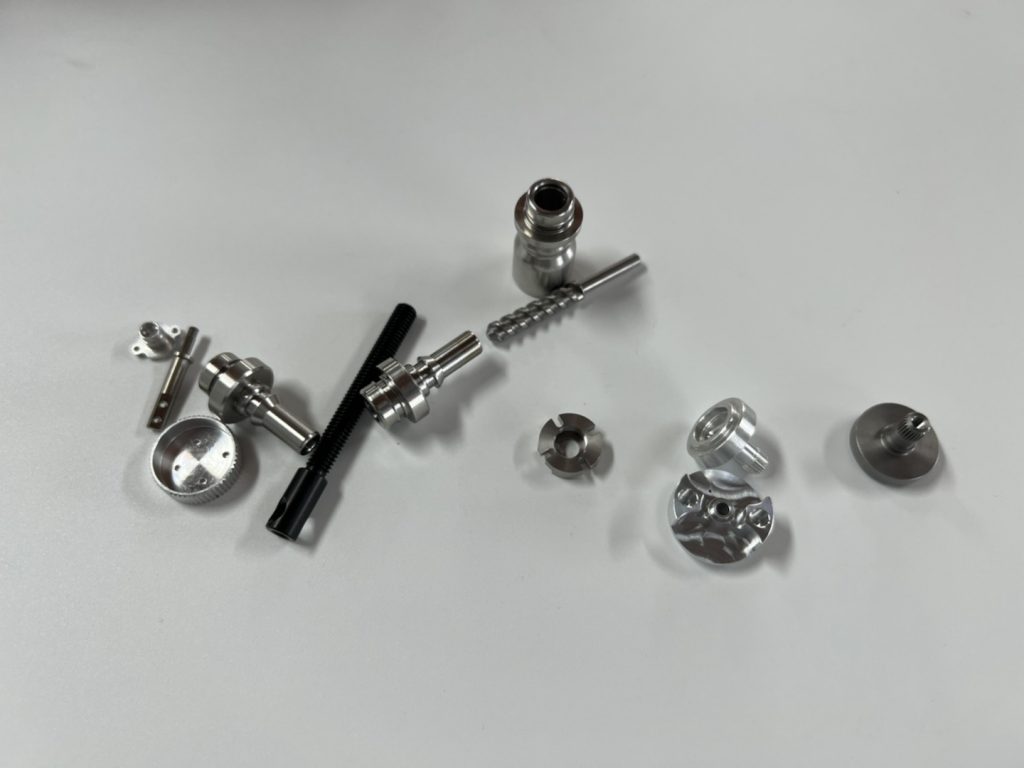
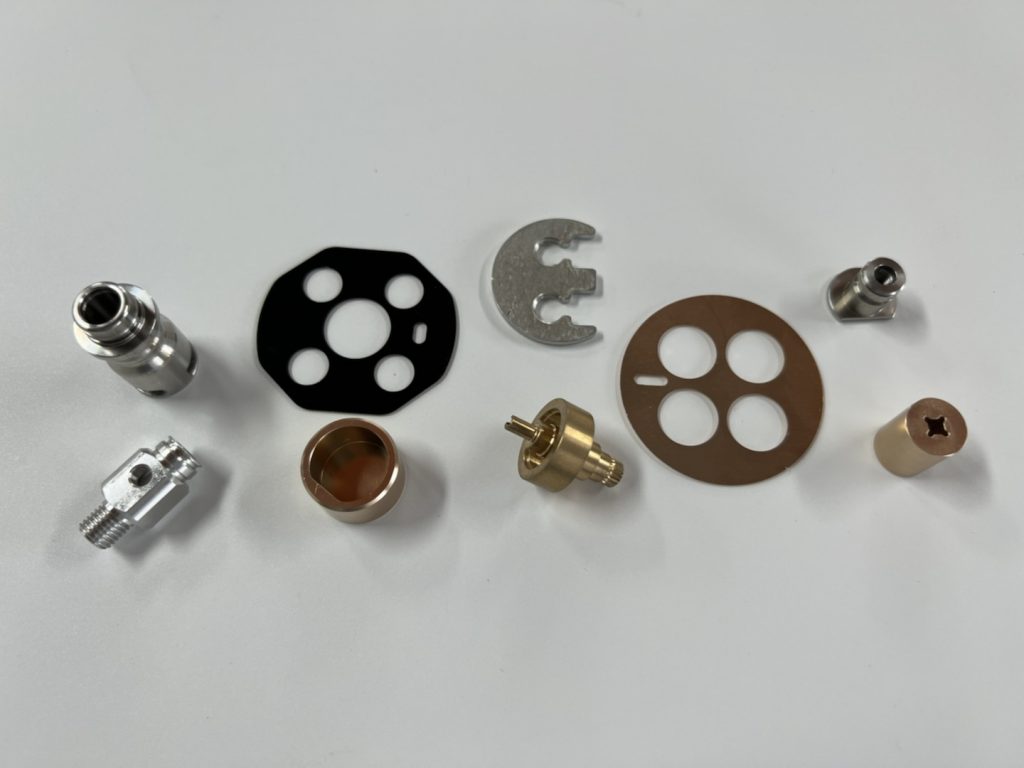


CNC turning materials options
- ABS
- Acrylic
- POM
- Nylon
- Teflon
- PVC
- Polystyrene
- Ultem
- Polyethylene
- Lexan/Polycarbonate
- PEEK
- PTFE
- Aluminum 6082
- SS 316
- C45
- Aluminum 6061
- SS 303
- Q235
- Aluminum 7075
- SS 304
- A2 Steel
- Aluminum 5083
- SS 301
- S355J2
- Aluminium 6060
- E-Cu57
- S235JR
- Aluminium 2017A
- CuZn39Pb3
- 42CrMo4
- MIC Aluminum
- Ti-6Al-4V
- 16MnCr5
CNC Turning Tolerance at Prepart
| Metals With Drawing | Plastics With Drawing | No Drawing | |
| Linear Dimension | +/- 0.01 mm | +/- 0.05 mm | ISO 2768 Medium |
| +/- 0.0003 inch | +/- 0.002 inch | ||
| Hole Diameters | +/- 0.008 mm | +/- 0.05 mm | ISO 2768 Medium |
| (Not Reamed) | +/- 0.0003 inch | +/- 0.002 inch | |
| Shaft Diameters | +/- 0.004 mm | +/- 0.05 mm | ISO 2768 Medium |
| +/- 0.00016 inch | +/- 0.002 inch |

CNC Turning Parts Surface Treatment Options at Prepart

| Anodizing Type III | Polishing |
| Anodizing Type III | Black Oxide |
| Chromate Plating | QPQ |
| As Machined | Zinc Plating |
| Bead Blasted | Nickel Plating |
| Heat treatment | Powder Coating |
| Thread Inserts | Laser Engraving |
Why Chosse prepart with cnc turning service
Flexible mfg
quick quote
From 1 pcs
Good QUALITY
COST EFFECTIVE
best SERVICES
DFM report
SATISFACTION
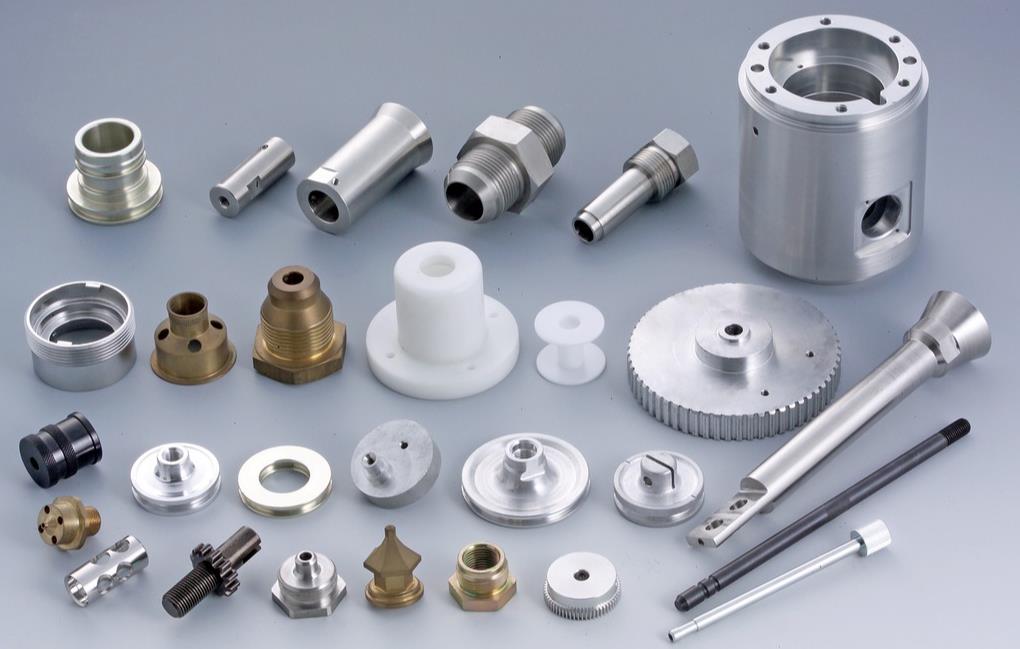
Case Applications Of CNC Turning









Here are ten application cases where CNC turning parts are commonly used:
1. Automotive Industry: CNC turning is used to manufacture various components in the automotive sector, including shafts, axles, pistons, and engine parts.
2. Aerospace Industry: Precision parts like turbine blades, aerospace connectors, and hydraulic components are produced through CNC turning to meet the stringent requirements of the aerospace industry.
3. Medical Devices: CNC turning is employed to create intricate parts for medical devices such as surgical instruments, implant components, and precision medical connectors.
4. Electronics: Connectors, pins, and housings for electronic devices are often manufactured using CNC turning for accurate dimensions and fine tolerances.
5. Oil and Gas Industry: CNC turning is used to create components for oil rigs, including valves, threaded fittings, and drilling equipment parts.
6. Hydraulics and Pneumatics: Cylinder rods, pistons, and other hydraulic and pneumatic components are produced using CNC turning for precise fit and function.
7. Industrial Machinery: Many parts of industrial machinery, including gears, bushings, and couplings, are manufactured using CNC turning for durability and precision.
8. Consumer Goods: CNC turning is used in producing components for various consumer products like faucets, knobs, and handles.
9. Textile Industry: CNC turned parts are used in textile machinery, such as spindles and rollers, to ensure smooth and precise operation.
10. Renewable Energy: CNC turning is applied in creating parts for renewable energy systems, including wind turbine components and solar panel mounts.
CNC Turning Machining Equipment at Prepart
CLX 450 * 10 Sets
CLX 750 * 5 Sets
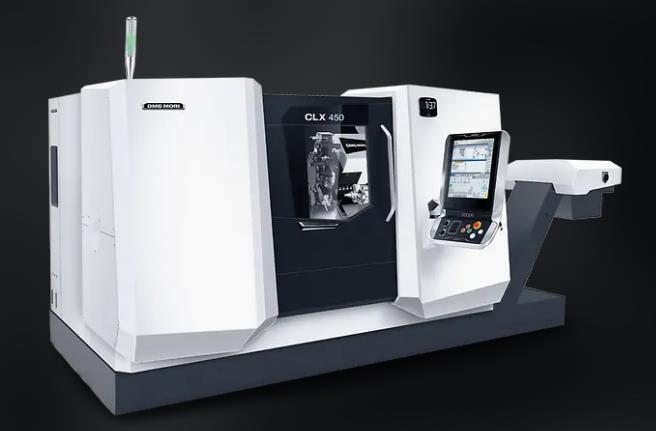

Max. workpiece diameter 400 mm
Max. workpiece length 800 mm
Max. bar capacity diameter 80 mm
Max. X-axis stroke 276 mm
Max. Y-axis stroke 120 mm
Max. Z-axis stroke 755 mm
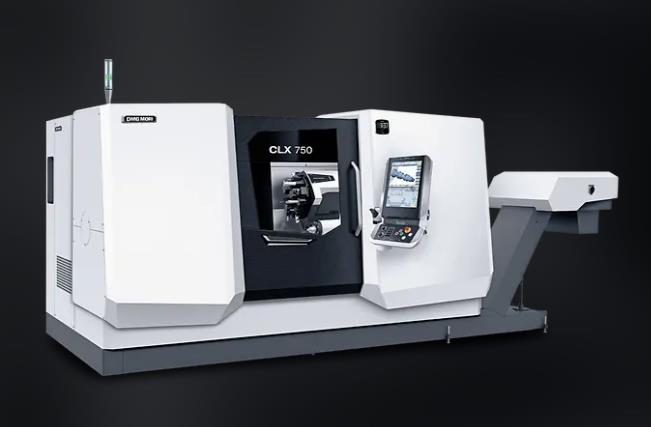

Max. workpiece diameter 700 mm
Max. workpiece length 1,300 mm
Max. bar capacity diameter 127 mm
Max. X-axis stroke 435 mm
Max. Y-axis stroke 160 mm
Max. Z-axis stroke 1,300 mm
Understanding CNC Turning: Is it the Right Choice for Your Part?
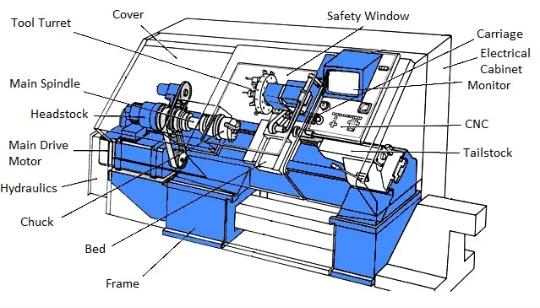
CNC turning is a process in which a cutting tool is used to remove material from a rotating workpiece to create a desired shape or form. Unlike traditional turning, CNC turning is automated and computer-controlled, which allows for greater precision, accuracy, and repeatability. CNC turning machines can work with a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Parts that can benefit from CNC turning are those with circular or cylindrical shapes, such as screws, bolts, and shafts. However, CNC turning can also produce more complex shapes and designs, including tapped holes, threads, and slots. Another advantage of CNC turning is that it can produce high-quality surface finishes, which are important for parts that require good friction and wear resistance.
So, how do you know if your part is a good fit for CNC turning?
The first factor to consider is the size of the part. CNC turning machines can handle a range of sizes, but parts that are too small or too large may not be a good fit. Additionally, the type of material and the required precision are important considerations. Parts that require tight tolerances or have complex geometries may benefit from CNC turning, but parts that require more flexibility or customization may be better suited for other manufacturing processes.
Another factor to consider is the cost. CNC turning is a more expensive process than traditional turning, so it may not be cost-effective for smaller production runs. Additionally, CNC turning requires specialized programming and setup, which can add to the cost and lead time. However, for larger production runs and complex parts, the benefits of CNC turning may outweigh the upfront costs.

Advantages of Prepart's CNC Turning Services
Precision and Accuracy
Prepart’s CNC turning services allow for high accuracy and precision during the manufacturing process. CNC turning utilises a computerised machine tool to execute high-speed machining which produces parts with exceptional accuracy and repeatability. The machines can also be programmed to make the same part repeatedly with the same dimensions ensuring consistency and reliability in the final product.
Increased Efficiency
CNC turning machines are capable of mass-producing parts with minimal human intervention. Prepart’s CNC turning services are designed for high-volume production runs that make it easier to complete large orders in a timely and efficient manner. The machines can run for hours at a time without interruption, increasing productivity and output.
Versatility
Prepart’s CNC turning services can produce parts of varying sizes, shapes and materials. They can also produce parts with intricate designs and complex geometries that would be difficult to make through traditional manufacturing methods. CNC turning machines can work with materials including aluminum, brass, copper, steel, and titanium. They can work on materials that are soft to extremely hard, which makes them ideal for producing a wide variety of parts.
Cost-Effective
CNC turning machines reduce material wastage, increase efficiency, and lower human labour costs. The machines can also operate for hours without interruption, minimising the need for human intervention which is costly over time. Prepart’s CNC turning services are less labour-intensive which results in reduced labour costs without sacrificing the quality of the final product.
Customised Parts
Prepart’s CNC turning services can produce customised parts to meet the exact specifications of their clients. CNC turning machines allow manufacturers to create parts that have unique shapes that are customised for specific applications. This versatility makes CNC turning ideal for producing parts for specialised industries with unique needs.
Some Design Tips to Help You Create CNC Turning-friendly Parts:
Keep It Symmetrical: Design parts with symmetry whenever possible. Symmetrical shapes reduce the complexity of machining, leading to improved accuracy and reduced production time.
Minimize Overhangs: Avoid long overhangs or unsupported features, as they may lead to vibration and deflection during machining. Keeping overhangs to a minimum improves machining stability.
Avoid Sharp Internal Corners: Internal sharp corners can be challenging to machine with standard turning tools. Use fillets or radii to ease machining and prevent tool breakage.
Choose Suitable Tolerances: Consult with your CNC turning service provider to determine appropriate tolerances for your design. Tight tolerances may increase production costs, so use them only where necessary.
Select Machinable Materials: Opt for materials that are easy to machine, like aluminum, brass, and mild steel. Avoid materials with excessive hardness or tough-to-machine properties unless necessary.
Design for Tool Accessibility: Ensure that cutting tools can access all required features of the part. Avoid deep cavities or complex features that may be difficult to reach with standard tooling.
Consider Material Wastage: Design parts to minimize material wastage during machining. Optimizing the stock material size and using efficient nesting can save costs and reduce material waste.
Provide Adequate Clearance: Ensure sufficient clearance between the rotating workpiece and the lathe’s chuck and tool holders to prevent collisions during machining.
Avoid Undercuts: Undercuts may require additional tool changes or special tooling, which can increase production time and costs. Minimize or eliminate undercuts in your design.
Use Standard Tool Sizes: Design features that can be machined with standard tool sizes. Custom tooling can increase production costs and lead times.
Add Chamfers and Radii: Include chamfers or radii on external edges to prevent sharp edges, reduce stress concentrations, and improve aesthetics.
Consider Part Orientation: Think about the best orientation for machining the part. Rotating the part to access different features can be time-consuming, so try to minimize the number of setups required.
Test Prototypes: Before proceeding with a large production run, create a prototype to test the design for functionality and identify potential issues in the manufacturing process.